Authors: Taylor Viggiano, MD – Lori Roust, MD – Holly Geyer, MD
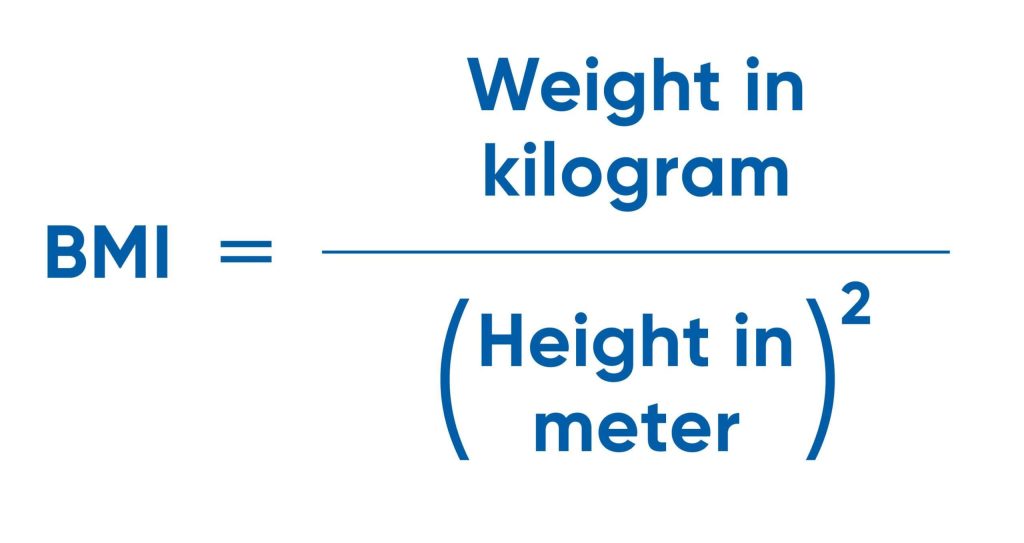
The classification of obesity is further divided into classes based upon BMI. These categories help in assessing the severity of obesity and associated health risks. Obesity has increased dramatically since the 1980s. In the United States, approximately 1 out of 3 of adults and 1 out of 6 of children and adolescents are classified as obese.
It’s important to know that BMI has some limits. It doesn’t tell us the difference between fat and muscle. For example, athletes might have a high BMI because they have a lot of muscle, but that doesn’t mean they are unhealthy. On the other hand, some people with a normal BMI might still have too much body fat.
What happens in the body
Obesity is linked to chronic low-grade inflammation, mainly caused by excess fatty tissue. This inflammation can cause insulin resistance, a major factor in the development of type 2 diabetes, and increase the risk of heart disease. Moreover, obesity can raise levels of estrogen, which is associated with a higher risk of certain cancers, particularly postmenopausal breast cancer.
Risk Factors
People develop obesity due to a combination of genetic, environmental, behavioral, and metabolic factors. Poor diet choices, high in calories and low in nutrients, along with a lack of physical activity, are major contributors. Genetics can influence how the body stores fat, and certain conditions or medications can also lead to weight gain. Additionally, stress, sleep deprivation, and a sedentary lifestyle play roles in disrupting normal metabolism, further contributing to obesity. Ultimately, it is the interplay of these factors that can lead to excessive weight gain and the development of obesity.
- Genetics can influence weight.
- Eating a poor diet composed of high-calorie, low-nutrient foods can lead to weight gain.
- Lack of exercise
- Age
- Limited access to healthy foods and exercise opportunities can increase the risk of developing obesity.
- Stress, depression, and poor sleep can lead to overeating.
- Certain health issues, like hypothyroidism or hormonal disorders, can affect weight.
- Some medications can cause weight gain as a side effect.
Symptoms of Obesity
Obesity can lead to a variety of health issues and symptoms. Common symptoms include feeling very tired, having trouble breathing, experiencing back pain, dealing with joint pain (like arthritis), sweating a lot, having difficulty sleeping, feeling sad.
Over time, obesity can also lead to serious health issues like type 2 diabetes, high cholesterol, and high blood pressure. It can affect the heart, making it work harder and increasing the risk of heart attacks and strokes. Some people with obesity may also have breathing problems at night, like obstructive sleep apnea. Further, obesity can lead to liver disease and gallbladder disease. Low testosterone can be associated with obesity.
Obesity raises the risk of several types of cancer, such as breast, uterine, kidney and GI tract cancers, especially when there is extra fat located around the waistline.
© 1998-2024 Mayo Foundation for Medical Education and Research (MFMER). All rights reserved

Sign up for Updates
To stay up to date please provide your email address.
-
By giving us your email you are opting-in to receive news and promotions
Sign up for Updates
To stay up to date please provide your email address.
-
By giving us your email you are opting-in to receive news and promotions







